With global climate change and population growth, water shortage has become a global challenge. As a crucial engineering measure for the utilization of water resources, the operation and management of reservoir is directly related to the ecological health of river basin and human life. However, conventional reservoir operation is difficult to balance the human benefit and ecological demands below the dam. Ecological operation of reservoir, a comprehensive analysis of trade-offs between economic benefit and downstream ecological needs, is of great significance for the sustainable utilization of multipurpose reservoir and the healthy development of river basin.
Construction and operation of large reservoirs has inevitably changed the processes of dam discharge volume and dam discharge temperature, thereby altering downstream natural river water temperature regimes. The alteration of water temperature threatens the overall hearth of downstream river ecosystem. Quantitative evaluation of dam-induced water temperature and ecological impacts, and reservoir ecological operation considering downstream ecological flow and ecological water temperature needs have become hotspot-forefront and challenging topics in the area of water resources management. However, appropriate evaluation method of ecological flow and ecological water temperature is still lacking. Meanwhile, with the increasing of management objectives and constraints, it is urgent to develop new optimization algorithms for pluralistic and complicated multi-objective reservoir ecological optimization operation.
The team of Professor Dong Wang and Professor Jichun Wu, from the School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Nanjing University, made a series of substantial progress in reservoir ecological optimization operation and management based on deep learning algorithms. The findings are as follows: (1) The water temperature prediction model based on artificial intelligence algorithms predicts river water temperature efficiently and reliably; (2) The deep learning-based evaluation method quantitatively separates the impacts of the Three Gorges Reservoir and climate change on the water temperature at Yichang in the middle reach of the Yangtze River when the data is limited; (3) By coupling with the two-dimensional hydrodynamic water temperature model and the suitability model, the habitat simulation method effectively calculates the suitable ecological flow and ecological water temperature for the Four Major Chinese Carps spawning in the middle reach of the Yangtze River; (4) By integrating deep learning algorithm with improved multi-objective evolutionary algorithm, the multi-objective simulation-optimization method efficiently optimizes the complex reservoir operation. The optimal management schemes of dam discharge volume and dam discharge temperature are proposed for the Three Gorges reservoir to comprehensively balance the economic and downstream ecological benefits. The above studies provide new thoughts and methods to reservoir ecological operation and optimal management.
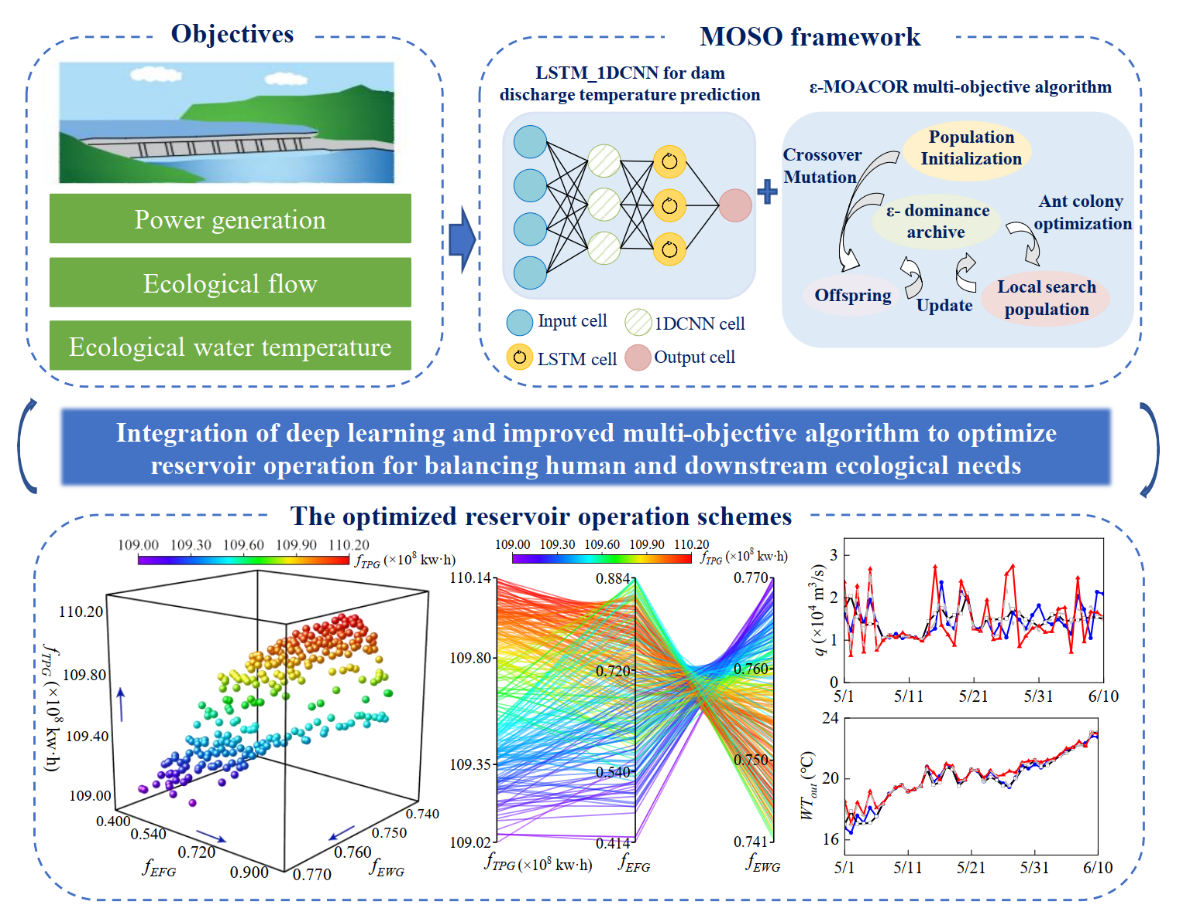
Fig. 1 Integration of deep learning and improved multi-objective algorithm to optimize reservoir ecological operation
Part of the above research findings were published in Science of The Total Environment, Ecohydrology, and Journal of Hydrology. The latest study was published in Water Research, a Nature Index Journal and leading journal in the water environmental sciences. Ph.D. student Rujian Qiu is the first author of the papers. Nanjing University is the corresponding leading institution. Collaborators include Professor Yuankun Wang from North China Electric Power University and Professor Vijay P. Singh from Texas A&M University. The studies were supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China, and National Natural Science Fund of China.
Links:
Qiu, R., Wang, D., Singh, V., Wang, Y., Wu, J., (2024). Integration of deep learning and improved multi-objective algorithm to optimize reservoir operation for balancing human and downstream ecological needs. Water Research, 253, 121314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2024.121314
Qiu, R., Wang, D., Singh, V., Zhang, H., Tao, Y., Wu, J., Wang, Y., (2023). Ecological responses of spawning habitat suitability to changes in flow and thermal regimes influenced by hydropower operation. Ecohydrology, 16(2), e2507. https://doi.org/10.1002/eco.2507
Qiu, R., Wang, Y., Rhoads, B., Wang, D., Qiu, W., Tao, Y., Wu, J., (2021). River water temperature forecasting using a deep learning method. Journal of Hydrology, 595, 126016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126016
Qiu, R., Wang, Y., Wang, D., Qiu, W., Wu, J., Tao, Y., 2020.Water temperature forecasting based on modified artificial neural network methods: Two cases of the Yangtze River. Science of The Total Environment, 737, 139729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139729

